Current booster ratings
Every car seat needs to be installed using either the lower anchors or a seat belt to secure it in place, never both. If you choose to use a seat belt to install your car seat, pay close attention to how to “lock” your seat belt according to the vehicle’s owner manual. With a forward-facing car seat, use a tether if one is available. Before installing your car seat make sure you understand the function and location of the vehicle and car seat parts that are used in installation.
Car Seats and Booster Seats
Car seats and boosters provide protection for infants and children in a crash, yet car crashes are a leading cause of death for children ages 1 to 13. That’s why it’s so important to choose and use the right car seat correctly every time your child is in the car. Follow these important steps to choose the right seat, install it correctly and keep your child safe.
Children killed in car crashes in 2021 who were unrestrained
of car seats and booster seats are used incorrectly
Find the Right Car Seat for Your Child
- Find The Right Car Seat
- The Process
- Car Seat Types
- Car Seat Recommendations
- Find and Compare Seats
- Parts and Tips
- Car Seat Installation Instructions
- Inspection
The Process
Follow these steps to help you through the process of finding the right car seat, installing it correctly, and keeping your child safe.
Find the right car seat
- Learn about the four car seat types
- Follow NHTSA’s car seat recommendations based on your child’s age and size
- Find and compare car seats and ease-of-use-ratings using NHTSA’s Car Seat Finder
Install your car seat correctly
- Understand the parts and tips used for installation
- Follow our detailed car seat installation instructions and videos
- Get your car seat inspected at a station nearest you
Keep your child safe in a car seat
- Register your car seat and sign up for recall notices to receive safety updates
Car Seat Types
Learn about the four types of car seats, while keeping in mind the following tips:
- As children grow, how they sit in your car will change. Make sure you use a car seat that fits your child’s current size and age.
- Not all car seats fit in all vehicles. Make sure the car seat is the right fit for your vehicle (PDF, 1.77 MB). Test the car seat you plan to buy to make sure it fits well in your vehicle.
- Buy a car seat that can be installed and used correctly every time.
Rear-Facing Car Seat

The best seat for your young child to use. It has a harness and, in a crash, cradles and moves with your child to reduce the stress to the child’s fragile neck and spinal cord.
Types
- Infant Car Seat (Rear-Facing only): Designed for newborns and small babies, the infant-only car seat is a small, portable seat that can only be used rear-facing. Most babies outgrow their infant seats before their first birthday. When that happens, we recommend that parents purchase a convertible or all-in-one car seat and use it rear-facing.
- Convertible Seat: As a child grows, this seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether. Because it can be used with children of various sizes, it allows for children to stay in the rear-facing position longer.
- All-in-One Seat: This seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat (with a harness and tether) and to a booster seat as a child grows. Because it can be used with children of various sizes, it allows for children to stay in the rear-facing position longer.
Forward-Facing Car Seat

Has a harness and tether that limits your child’s forward movement during a crash.
Types
- Convertible Seat: As a child grows, this seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether.
- Combination Seat: As a child grows, this seat transitions from a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether into a booster.
- All-in-One Seat: This seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat (with a harness and tether) and to a booster seat as a child grows.
Booster Seat

Raises and positions a child so the vehicle’s lap-and-shoulder belt fits properly over the stronger points of a child’s body, the hips and across the chest.
Types
- Booster Seat With High Back: This type of booster seat is designed to boost the child’s height so the seat belt fits properly. It also provides neck and head support and is ideal for vehicles that don’t have head rests or high seat backs.
- Backless Booster Seat: A backless booster seat is designed to boost the child’s height so the seat belt fits properly. It does not provide head and neck support. It is ideal for vehicles that have head rests.
- Combination Seat: As a child grows, this seat transitions from a forward-facing seat with a harness into a booster.
- All-in-One Seat: This seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat (with a harness and tether) and to a booster seat as a child grows.
Seat Belt

Should lie across the upper thighs and be snug across the shoulder and chest to restrain your child safely in a crash. It should not rest on the stomach area or across the neck or face.
Car Seat Recommendations
There are many car seat choices on the market. Use the information below to help you choose the type of car seat that best meets your child’s needs or print out NHTSA’s car seat recommendations for children (PDF, 370 KB).
- Select a car seat based on your child’s age and size, then choose a seat that fits in your vehicle, and use it every time.
- Always refer to your specific car seat manufacturer’s instructions (check height and weight limits) and read the vehicle owner’s manual on how to install the car seat using the seat belt or lower anchors and a tether, if available.
- To maximize safety, keep your child in the car seat for as long as possible, as long as the child fits within the manufacturer’s height and weight requirements.
- Keep your child in the back seat at least through age 12.
Recommended car seats based on your child’s age and size
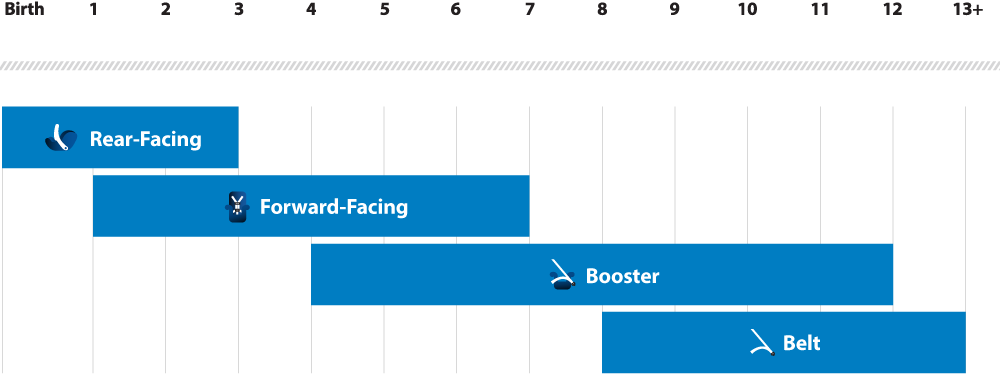
Rear-Facing Car Seat

Birth-12 Months
Your child under age 1 should always ride in a rear-facing car seat. There are different types of rear-facing car seats:
- Infant-only seats can only be used rear-facing.
- Convertible and all-in-one car seats typically have higher height and weight limits for the rear-facing position, allowing you to keep your child rear-facing for a longer period of time.
1 – 3 Years
Keep your child rear-facing as long as possible. It’s the best way to keep him or her safe. Your child should remain in a rear-facing car seat until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the rear-facing car seat, your child is ready to travel in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether.
Forward-Facing Car Seat

1 – 3 Years
Keep your child rear-facing as long as possible. It’s the best way to keep him or her safe. Your child should remain in a rear-facing car seat until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the rear-facing car seat, your child is ready to travel in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether.
4 – 7 Years
Keep your child in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the forward-facing car seat with a harness, it’s time to travel in a booster seat, but still in the back seat.
Booster Seat

4 – 7 Years
Keep your child in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the forward-facing car seat with a harness, it’s time to travel in a booster seat, but still in the back seat.
8 – 12 Years
Keep your child in a booster seat until he or she is big enough to fit in a seat belt properly. For a seat belt to fit properly the lap belt must lie snugly across the upper thighs, not the stomach. The shoulder belt should lie snugly across the shoulder and chest and not cross the neck or face. Remember: your child should still ride in the back seat because it’s safer there.
Seat Belt

8 – 12 Years
Keep your child in a booster seat until he or she is big enough to fit in a seat belt properly. For a seat belt to fit properly the lap belt must lie snugly across the upper thighs, not the stomach. The shoulder belt should lie snugly across the shoulder and chest and not cross the neck or face. Remember: your child should still ride in the back seat because it’s safer there.
Find and Compare Seats
Car Seat Finder Find the right car seat
Search car seats by brand name and model
Find car seats for your child by brand, or look up the details of a specific car seat model.
The Car Seat Finder is an easy-to-use tool that lets you compare seats and ease-of-use ratings to find the right car seat for your child. Just fill out your child’s age, height and weight above, and you’ll be provided car seat types that fit your child. Before you get started, make sure you’re familiar with the four types of car seats and NHTSA’s recommendations for choosing the right type of seat for your child.
Car Seat Installation Parts and Tips
Your child’s safety could be in jeopardy if your car seat is not installed correctly. Before you install your car seat, make sure you’re familiar with vehicle and car seat parts used in the installation process and these important installation safety tips.
Vehicle and Car Seat Parts Explained
Every car seat needs to be installed using either the lower anchors or a seat belt to secure it in place, never both. If you choose to use a seat belt to install your car seat, pay close attention to how to “lock” your seat belt according to the vehicle’s owner manual. With a forward-facing car seat, use a tether if one is available. Before installing your car seat make sure you understand the function and location of the vehicle and car seat parts that are used in installation.
Vehicle Parts
Lower Anchors
Used for installing a car seat using its lower anchor attachments
The lower anchors are found in a minimum of two rear seating positions in a vehicle. Each lower-anchor-equipped seating position has two small horizontal bars found in the space between the vehicle seat’s back and bottom cushion (the “seat bight”).
Tether Anchor
Used for attaching a car seat’s tether to the vehicle
Typically there are a minimum of three tether anchors in a vehicle. In sedans, these are usually located above/behind the vehicle’s back seat on the rear shelf. In some larger vehicles such as vans, pickup trucks, and SUVs, these tether anchors may be found on the back of a vehicle seat, on the floor, the ceiling, or other location.
To avoid confusing tether anchors with other hardware such as luggage tie-downs, be sure to read your vehicle’s owner manual carefully to find out where they are located in your particular vehicle.
Car Seat Parts
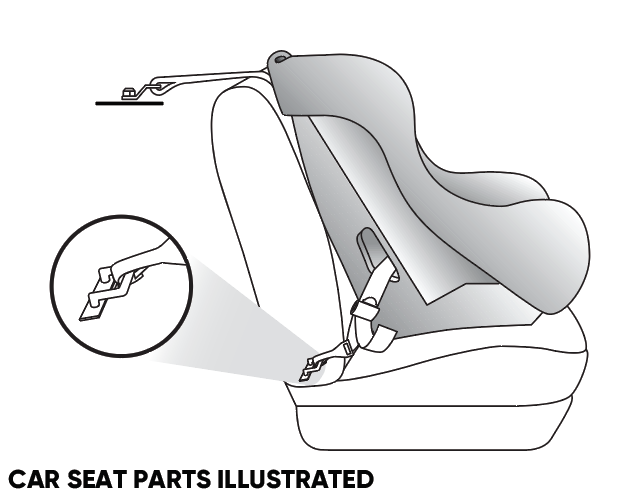
Attach top tether from the car seat to the tether anchor in the vehicle.
Fasten lower anchor attachments on the car seat to the lower anchors in the vehicle.
Lower Anchor Attachments
Used to install the car seat in a vehicle with lower anchors
Tether
Used to secure a forward-facing car seat and limit forward head movement in a crash
The tether is located on the top rear of convertible, combination, and all-in-one car seats. It’s adjustable and has a hook and strap that connects to one of your vehicle’s tether anchors. Most rear-facing car seats in the United States do not use a tether for installation. However, installations vary from model to model, so you must review your particular car seat’s instructions and your vehicle’s owner manual carefully.
Follow your car seat manufacturer’s instructions regarding when and how to use the tether for your particular seat. NHTSA recommends always using a tether with a forward-facing car seat—installed with your vehicle’s seat belt OR the lower anchors—as long as it is permitted by both the car seat and vehicle manufacturers. IMPORTANT: Both installation methods are designed to work with the tether to achieve the highest level of safety for child passengers restrained in forward-facing car seats.
Lower Anchor Weight Limits
Lower anchors have weight limits set by the vehicle and car seat manufacturers. You can determine the lower anchor weight limit by checking the warning label or installation diagrams located on the side of the car seat. If your car seat does not have a label, you can determine the maximum allowable child weight for lower anchor use by subtracting the weight of the car seat (usually available in the car seat’s instruction manual) from 65 pounds.
Lower anchor weight limit = 65 lbs – weight of car seat
Know the Facts
Once your child outgrows the vehicle or car seat manufacturer’s established limits for the lower anchors, stop using the lower anchor attachments and reinstall the car seat using the vehicle’s seat belt.
Current booster ratings
IIHS ratings take the guesswork out of selecting boosters most likely to provide good lap and shoulder belt fit in a range of vehicles. Unlike child restraints with built-in harnesses, booster seats rely on vehicle safety belts to restrain children. Boosters are supposed to make adult belts fit children better and are for kids who have outgrown their forward-facing restraints.
The Institute puts the booster seats it tests into four categories:
- BEST BETs are seats that provide good belt fit for typical 4 to 8 year-olds in almost any car, minivan or SUV.
- GOOD BETs provide acceptable belt fit in most cars, minivans or SUVs.
- Not Recommended don’t provide good belt fit and should be avoided. There are currently no boosters on the market with this designation.
- Check Fit applies to booster seats the Institute has tested that have varied results depending on child size and vehicle model.
Proper fit is key
Our ratings identify boosters most likely to provide good lap and shoulder belt fit. Safety belts are designed with adults in mind, not kids, but when a booster seat is doing its job, the vehicle belt will fit a child correctly. That means the lap belt will lie flat across a child’s upper thighs, not across the soft abdomen, and the shoulder belt will cross snugly over the middle of a child’s shoulder.
Checking booster fit
Both the lap and shoulder belts must fit your child correctly.
Lap belt fit — The lap belt should lie flat and on top of the thighs, not higher up on the abdomen.

Good lap belt fit:
outline = arm rest removed to show belt position
Poor lap belt fit:
outline = arm rest removed to show belt positionShoulder belt fit — The shoulder belt should fit snugly across the middle of the child’s shoulder. If it falls off the shoulder or rests on your child’s neck, it won’t work as well. An improper fit could encourage your child to move the belt to a dangerous position, such as behind the back or under the arm.

Good shoulder belt fit

Poor shoulder belt fit

Poor shoulder belt fit
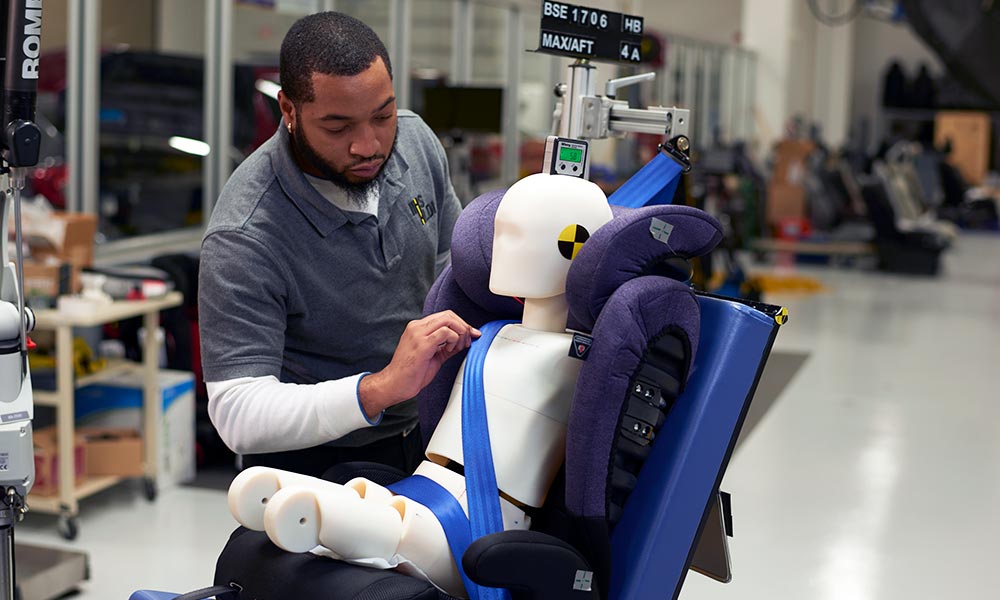

Test protocol
IIHS assesses boosters using a special dummy representing an average-size 6 year-old. Engineers measure how three-point lap and shoulder belts fit the dummy in each of the tested boosters under four conditions that span the range of safety belt configurations in vehicle models. An overall rating for each booster is then assigned based on the range of scores for the lap and shoulder belt measurements.
